The most basic yuri plotline — what publisher Erica Friedman calls “Story A” — traces its roots back to the pioneering Class S fiction of Nobuko Yoshiya (1896-1973). In works such as Hana monogatari (1916-24) and Yaneura no nishojo (1919), schoolgirls developed intense, often romantic, feelings for other schoolgirls. Given the period in which Yoshiya wrote, it’s not surprising that her characters’ relationships were never consummated; the girls might exchange passionate letters or meaningful glances, but marriage, graduation, or death prevented them from being together as a couple. Fifty years later, when manga artists such as Ryoko Yamagishi and Riyoko Ikeda began writing girls’ love stories, they, too, favored tragic endings; Yamagishi’s Shiroi Heya no Futari (1971), for example, culminates in a melodramatic death (suicide by ex-boyfriend, to be exact), as do Ikeda’s Oniisama e… (1975) and Claudine…! (1978).
Small wonder, then, that manga-ka Rica Takashima saw a vacuum that needed filling. “There were very few manga with lesbian stories,” Takashima explains in the afterword to Rica ‘tte Kanji!? “Only depressing, sad stories about ‘forbidden love’ and with a break-up in the end. For example, ‘If I were a man, I could marry you.’ That kind of thing, but I wanted to read a HAPPY story.”
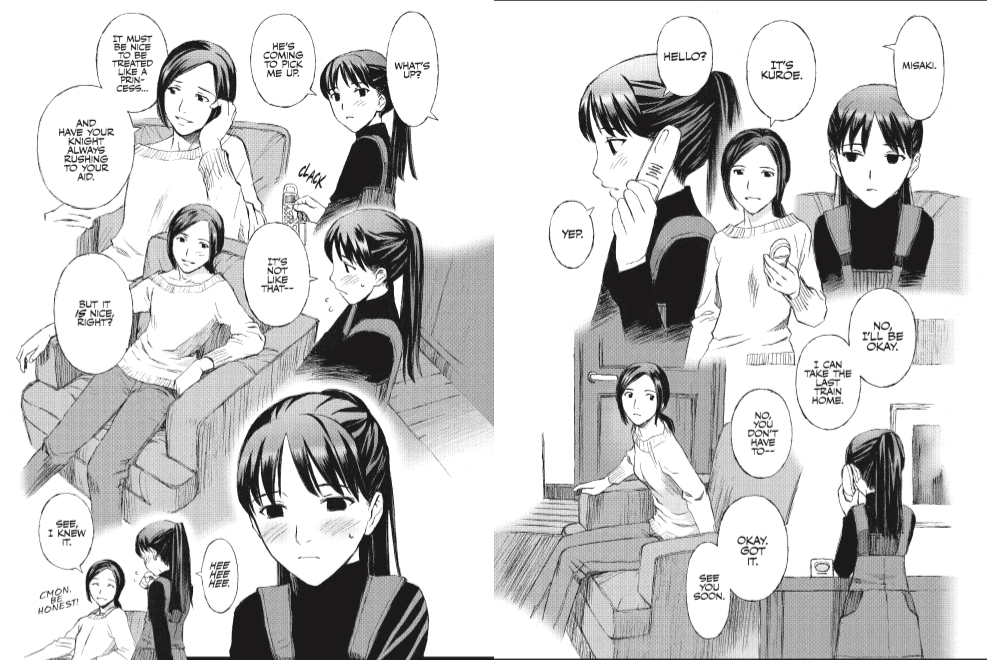
And “happy” is the perfect adjective to describe Rica ‘tte Kanji!? Rica, the heroine, is a cheerful optimist who moves to Tokyo to attend junior college (she plans to major in early childhood development) and explore the Nichome district, home to the city’s gay community. At the beginning of the series, Rica is nervous about visiting Nichome for the first time, worrying about what to wear and how to handle pick-up lines:
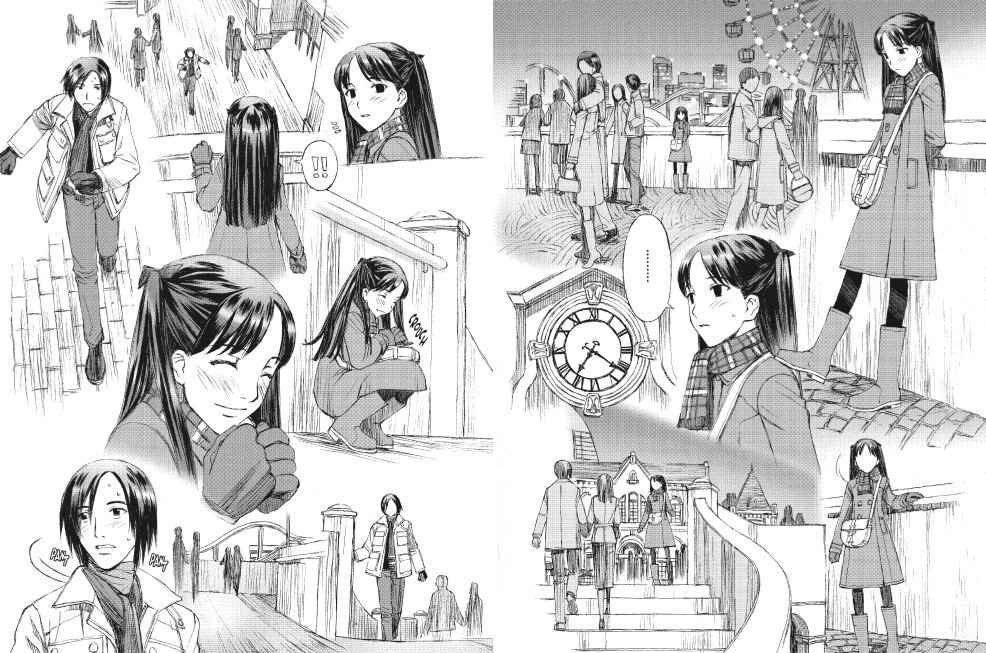
Rica’s fears are quickly allayed when she’s introduced to Miho, a sardonic art student a few years Rica’s senior. The two meet cute on Rica’s first trip to Nichome’s Lily Bar, where Rica confesses that she’s never met “an actual lesbian.” “I grew up out in the country,” she explains to Miho. “It’s the same for everyone in the beginning,” Miho assures her, prompting Rica to declare Miho her first gay friend. Though Miho falls for Rica right away, Rica’s lack of experience and general ditziness makes her oblivious to Miho’s advances. Their relationship has another hurdle to clear as well: Rica is just as nervous about the idea of having sex as she was about making a good impression at the Lily Bar, and keeps Miho at arm’s length — figuratively and literally — as she tries to decide what she’s comfortable doing.
What Takashima does better than most is to find the comedy in these situations, not by creating artificial misunderstandings between the characters, or manufacturing romantic rivals, but by making us privy to Rica and Miho’s thoughts. The two women’s internal monologues are funny, peppered with cute and weird observations, but they’re also very truthful; who among us hasn’t worried about putting the moves on a friend or being naked with a new partner?
Though Takashima’s script is charming, what really makes Rica ‘tte Kanji!? work is the art. That may seem like a funny thing to say about a story in which the characters are little more than well-dressed stick figures with cute, round faces, but Takashima’s illustrations have a warm, handmade quality. Better still, the artwork never panders to male yuri fans; by rendering the characters as cute, paper-doll figures, Takashima directs the eye away from Rica and Miho’s bodies towards their faces, compelling the reader to see the women as two people fumbling through a relationship, not fantasy objects.
And speaking of fantasy, a few reviewers have pointed out the absence of real conflict in Rica ‘tte Kanji!?. Though Miho and Rica’s relationship hits a few minor snags, their romance takes place in a bubble untouched by homophobia or workaday concerns. It’s a fair criticism, I suppose, but one that misses the point; Rica ‘tte Kanji!? is a cheeky, cheerful rebuke to the Tragic Gay Story, substituting a happily-ever-after ending for death and separation.
Impatient readers can find copies of Rica ‘tte Kanji on Amazon for about $24.00. If you’re willing to wait a few months, however, ALC Publishing will be releasing a new omnibus edition that will include the original Rica ‘tte Kanji stories, as well as material written for ALC’s Yuri Monogatari anthologies.
RICA ‘TTE KANJI!? • BY RICA TAKASHIMA • ALC PUBLISHING • 96 pp.