“When he heard his cry for help, it wasn’t human” — so went the tagline for Ken Russell’s Altered States (1980), a bizarre fever-dream of Nietzchean philosophy, horror, and mystical hoo-ha in which a scientist’s experiments result in his spontaneous devolution. That same tagline would work equally well for Osamu Tezuka’s Ode to Kirihito (1970-71), a globe-trotting medical mystery about a doctor who takes a similar step down the evolutionary ladder from man to beast. In less capable hands, Kirihito would be pure, B-movie camp with delusions of grandeur — as Altered States is — but Tezuka synthesizes these disparate elements into a gripping story that explores meaty themes: the porous boundaries between man and animal, sanity and insanity, godliness and godlessness; the arrogance of scientists; and the corruption of the Japanese medical establishment.
At its most basic level, Ode to Kirihito is a beat-the-clock thriller in which a charismatic young doctor named Kirihito Osanai tries to discover the cause of Monmow, a mysterious condition that reduces its victims to hairy, misshapen creatures with dog-like snouts. Kirihito’s superior, the ambitious Dr. Tatsugaura, dispatches Kirihito to Doggodale, a remote mountain village where hundreds of residents have developed suggestive symptoms. Once in Doggodale, Kirihito contracts Monmow himself, thus beginning a hellish odyssey to escape the village, arrest the disease’s progress, and share his findings with the medical community.
 At a deeper level, however, Ode to Kirihito is an extended meditation on what distinguishes man from animal. Kirihito’s physical transformation forces him to the very margins of society; he terrifies and fascinates the people he encounters, as they alternately shun him and exploit him for his dog-like appearance. (In one of the manga’s most engrossing subplots, an eccentric millionaire kidnaps Kirihito for display in a private freak show.) The discrimination that Kirihito faces — coupled with Monmow’s dramatic symptoms, such as irrational aggression and raw meat cravings — lead him to question whether he is, in fact, still human. Throughout the story, he wrestles with a strong desire to abandon reason and morality for instinct; only his medical training — and the ethics thus inculcated — prevent him from embracing the beast within.
At a deeper level, however, Ode to Kirihito is an extended meditation on what distinguishes man from animal. Kirihito’s physical transformation forces him to the very margins of society; he terrifies and fascinates the people he encounters, as they alternately shun him and exploit him for his dog-like appearance. (In one of the manga’s most engrossing subplots, an eccentric millionaire kidnaps Kirihito for display in a private freak show.) The discrimination that Kirihito faces — coupled with Monmow’s dramatic symptoms, such as irrational aggression and raw meat cravings — lead him to question whether he is, in fact, still human. Throughout the story, he wrestles with a strong desire to abandon reason and morality for instinct; only his medical training — and the ethics thus inculcated — prevent him from embracing the beast within.
Tezuka explores the boundaries between the rational and the instinctual in other ways as well. Running in tandem with Kirihito’s metamorphosis is another devolution of sorts: Kirihito’s colleague Dr. Urabe, who descends into madness after uncovering a sinister plot within the administration of M University Hospital. When we first meet Urabe, he’s a self-interested cad who lusts after Kirihito’s fiancee Izumi, views Kirihito as more rival than friend, and lacks the will to challenge Tatsugaura, even when data suggests Tatsugaura’s hypothesis about Monmow is flat-out wrong. The slow dawning of Urabe’s conscience, however, precipitates a dramatic change; his psyche splits in two, with one half striving after truth and the other succumbing to base impulse. Even as Urabe begins to redeem himself, collaborating with Izumi to reveal Tatsugaura’s dishonesty, he frequently lapses into savage, sexual aggression.
Other characters’ reactions to these transformations — especially characters in positions of authority or power — provide Tezuka with ample opportunity to engage in one of his favorite activities: exposing institutional hypocrisy. The scandal surrounding Tatsugaura’s Monmow hypothesis, for example, lays bare the corruption within the barely fictional Japanese Medical Association. In his relentless quest to become head of the organization, Tatsugaura seeks to establish an international reputation as an infectious disease expert, even going so far as to suppress evidence that contradicts his thesis. Yet the revelation of Tatsugaura’s deceit does little to jeopardize his position among his peers; only the young doctors find his behavior objectionable, yet they cannot dislodge him from his powerful position.
One of the key figures in revealing Tatsugaura’s treachery, Sister Helen, also provides Tezuka a chance to tear away the veil of hypocrisy from another institution — in this case, the Catholic Church. Midway through the first volume, a priest attempts to murder Sister Helen after she contracts Monmow disease. When confronted with his act, he acknowledges his intent but denies his purpose was evil; he insists on protecting the Church’s reputation at all costs, fearing that news of Helen’s condition would bring a scandal, as the received wisdom about Monmow disease held that Caucasians were immune to it.
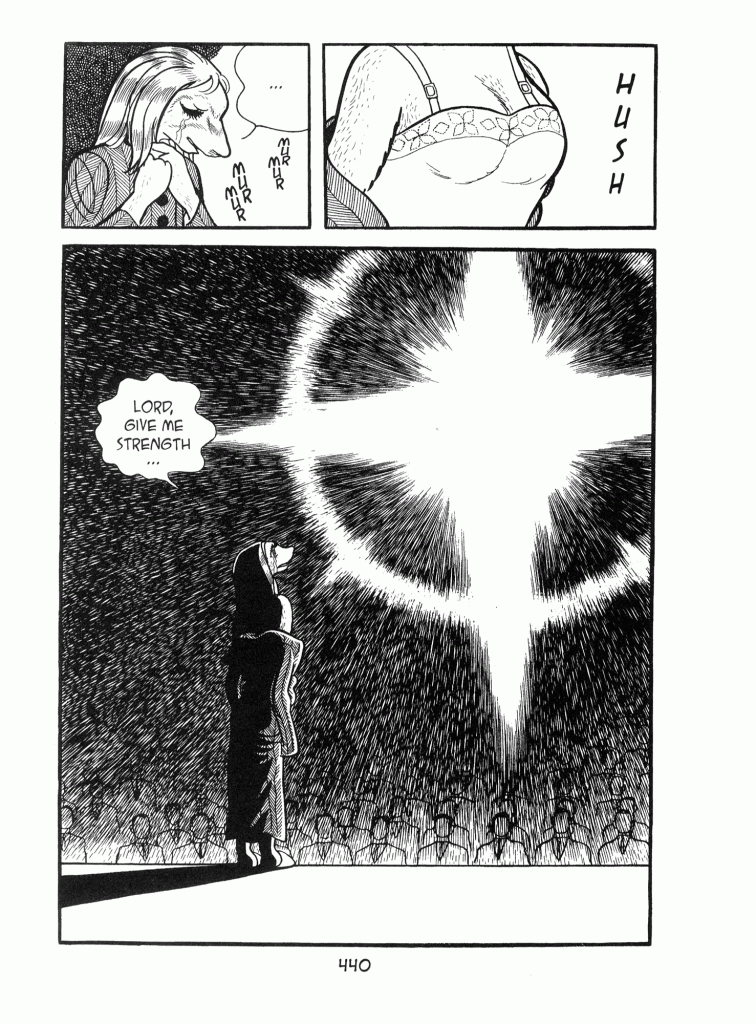
At the same time, however, Tezuka uses his characters’ metamorphoses to reveal the human capacity for selflessness and spirituality. Sister Helen provides the most obvious example; after entertaining thoughts of suicide, she has an epiphany — literally, as the cross imagery above suggests — and begins emulating Christ’s example, eventually finding her place ministering to the residents of an impoverished industrial town. Other characters demonstrate a similar capacity for selfless behavior: Urabe, for example, devotes himself to finding Kirihito, while Reika, a circus performer, helps Kirihito escape from captivity and reassert his humanity by practicing medicine.
One could certainly view Ode to Kirihito as heavy-handed allegory; there’s nothing subtle about its Christian imagery or Elephant Man storyline. Yet Tezuka’s fondness for Baroque subplots, over-the-top action sequences, and larger-than-life villains demands an equally bold approach for exploring the story’s greater themes. After all, Kirihito features dog men, sideshow freaks, an evil millionaire who hosts his own private circus, a German geneticist sporting a monocle, and an acrobat who risks life and limb to become human tempura; had Tezuka played things straight, or tried to state his man-vs-inner-beast conflict in less obvious terms, the story would seem preposterous and arty, a surreal experiment devoid of genuine human feeling.
As he would do in MW (1976-78), Tezuka pushes the boundaries of the comics medium in Ode to Kirihito, aiming for a cinematic style capable of immersing us not only in the action but in the characters’ own thought processes. Though Kirihito has its share of artfully staged chases, fights, and dramatic confrontations, the most visually arresting sequences depict Urabe’s fragile mental state:

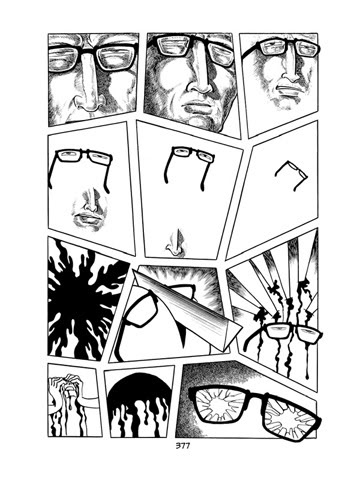
The panel shapes alone are a brilliant stroke; not only do they suggest his fractured and chaotic thought process, they also have a hint of the insect about them, as if we’re viewing Urabe’s consciousness through a fly’s eye. The knife and blood imagery are cliche, to be sure, but the shattered glasses are a novel and unsettling gesture open to multiple interpretations. Even the more conventional sequence on the left, in which Urabe leaves a hospital in a murderous rage, employs its share of neat visual tricks: Tezuka dramatizes Urabe’s personality shift by rotating the character’s image until he appears to be walking through an upside-down hall of mirrors. Amplifying the effect is the ambiguous way in which Tezuka draws Urabe’s legs in the bottom panel; as Matthew Brady observed in his review of Ode to Kirihito, the image simultaneously evokes dripping blood and moving limbs.
Perhaps the best compliment I can pay Ode to Kirihito is to say that Tezuka achieves on paper what John Frankenheimer achieved on film with The Train, Seven Days in May, and The Manchurian Candidate, transforming the humble thriller into a vehicle for telling thought-provoking, challenging stories that enlighten as they entertain. Kirihito may not surpass the narrative sophistication or visual poetry of Phoenix, but it comes awfully close. A must-read for serious manga lovers.
Review copies provided by Vertical, Inc.
ODE TO KIRIHITO, VOLS. 1-2 • BY OSAMU TEZUKA • VERTICAL, INC. • RATING: OLDER TEEN (16+)
 As a feminist, yaoi puts me in a difficult position. On the one hand, I love the idea of women creating erotica for other women, of creating a safe and fun space where female readers can explore their sexual fantasies. (I don’t know about you, but Ron Jeremy has never factored into any of mine.) On the other hand, I’m often uncomfortable by the way in which rape is conflated with extreme romantic desire in yaoi; it’s disappointing to see the “you’re so irresistible, I couldn’t help myself!” defense trotted out as a justification for sexual violation. To be sure, the rape-as-love trope abounds in romance novels and mainstream pornography as well, but as a feminist, it makes me just as uncomfortable to encounter it in yaoi as it does to encounter it in an episode of General Hospital. Then, too, there’s the issue of the characters’ homosexuality, which is sometimes trivialized (i.e., they’re not gay, they’re just so good-looking they couldn’t help themselves!), ignored, or “explained” by a character’s tragic past, as if sexual orientation were a simple, situational decision.
As a feminist, yaoi puts me in a difficult position. On the one hand, I love the idea of women creating erotica for other women, of creating a safe and fun space where female readers can explore their sexual fantasies. (I don’t know about you, but Ron Jeremy has never factored into any of mine.) On the other hand, I’m often uncomfortable by the way in which rape is conflated with extreme romantic desire in yaoi; it’s disappointing to see the “you’re so irresistible, I couldn’t help myself!” defense trotted out as a justification for sexual violation. To be sure, the rape-as-love trope abounds in romance novels and mainstream pornography as well, but as a feminist, it makes me just as uncomfortable to encounter it in yaoi as it does to encounter it in an episode of General Hospital. Then, too, there’s the issue of the characters’ homosexuality, which is sometimes trivialized (i.e., they’re not gay, they’re just so good-looking they couldn’t help themselves!), ignored, or “explained” by a character’s tragic past, as if sexual orientation were a simple, situational decision. Oh, Natsume Ono, I just can’t quit you! I was not wild about
Oh, Natsume Ono, I just can’t quit you! I was not wild about  At first glance, Shirley looks like a practice run for Emma, a collection of pleasant, straightforward maid stories featuring prototype versions of William, Eleanor, and Emma. A closer examination, however, reveals that Shirley is, in fact, a series of detailed character sketches exploring the relationships between three maids and their respective employers. And while some of these sketches aren’t entirely successful — Kaoru Mori cheerfully describes one as “an extremely cheap story about a boy and an animal” — the five chapters focusing on thirteen-year-old Shirley Madison and her independent, headstrong employer are as good as any passage in Emma.
At first glance, Shirley looks like a practice run for Emma, a collection of pleasant, straightforward maid stories featuring prototype versions of William, Eleanor, and Emma. A closer examination, however, reveals that Shirley is, in fact, a series of detailed character sketches exploring the relationships between three maids and their respective employers. And while some of these sketches aren’t entirely successful — Kaoru Mori cheerfully describes one as “an extremely cheap story about a boy and an animal” — the five chapters focusing on thirteen-year-old Shirley Madison and her independent, headstrong employer are as good as any passage in Emma. Invoke Tezuka’s name, and most readers immediately think of Astro Boy, Buddha, and Princess Knight. But there’s a darker side to Tezuka’s oeuvre that dates back to 1953, the year in which he brought Dostoevsky’s tormented Raskolnikov to life in a manga-fied version of Crime and Punishment. It’s this side of Tezuka — the side that acknowledges the human capacity for violence, greed, and deception — that’s on display in MW, a twisty thriller about a sociopath and the priest who loves him.
Invoke Tezuka’s name, and most readers immediately think of Astro Boy, Buddha, and Princess Knight. But there’s a darker side to Tezuka’s oeuvre that dates back to 1953, the year in which he brought Dostoevsky’s tormented Raskolnikov to life in a manga-fied version of Crime and Punishment. It’s this side of Tezuka — the side that acknowledges the human capacity for violence, greed, and deception — that’s on display in MW, a twisty thriller about a sociopath and the priest who loves him. 10. THE DREAMING
10. THE DREAMING 9. OFF*BEAT
9. OFF*BEAT 8. BLUE MONDAY
8. BLUE MONDAY 7. JAPAN AI: A TALL GIRL’S ADVENTURES IN JAPAN
7. JAPAN AI: A TALL GIRL’S ADVENTURES IN JAPAN 6. EMPOWERED
6. EMPOWERED 5. 12 DAYS
5. 12 DAYS 4. KING CITY
4. KING CITY 3. YOKAIDEN
3. YOKAIDEN 2. NIGHTSCHOOL: THE WEIRN BOOKS
2. NIGHTSCHOOL: THE WEIRN BOOKS 1. SCOTT PILGRIM
1. SCOTT PILGRIM There are two things to know about Bride of the Water God before you begin reading: first, the artwork is stunningly beautiful, and second, the story takes frequent, confusing detours that are almost impossible to explain, given what we know about the characters. If you find yourself vacillating between “Oh, so pretty!” and “Sweet Jesus, that makes no sense!”, know that you’re not alone.
There are two things to know about Bride of the Water God before you begin reading: first, the artwork is stunningly beautiful, and second, the story takes frequent, confusing detours that are almost impossible to explain, given what we know about the characters. If you find yourself vacillating between “Oh, so pretty!” and “Sweet Jesus, that makes no sense!”, know that you’re not alone. First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author.
First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author. First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author.
First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author. Nico Hayashi, code name “Sexy Voice,” is a bit older than Harriet — Nico is 14, Harriet is 11 — but she’s cut from the same bolt of cloth, as Sexy Voice and Robo amply demonstrates. Like Harriet, Nico entertains fanciful ambitions: “I want to be a spy when I grow up, or maybe a fortune teller,” she informs her soon-to-be-employer. “Either way, I’m in training. A pro has to hone her skills.” Nico, too, has a spy outfit — in her case, comprised of a wig and falsies — and an assortment of “spy tools” that include her cell phone and a stamp that allows her to forge her parents’ signature on notes excusing her from school. Like Harriet, Nico hungers for the kind of adventure that’s supposed to be off-limits to girls, skipping school to pursue leads, analyzing a kidnapper’s ransom call, luring bad guys into traps. Most importantly, both girls are students of adult behavior. Both Harriet the Spy and Sexy Voice and Robo include a scene in which the heroine constructs detailed character profiles from a few snippets of conversation. The similarities between these moments are striking. In Fitzhugh’s book, Harriet visits a neighborhood diner, nursing an egg cream while listening to other customers’ conversations:
Nico Hayashi, code name “Sexy Voice,” is a bit older than Harriet — Nico is 14, Harriet is 11 — but she’s cut from the same bolt of cloth, as Sexy Voice and Robo amply demonstrates. Like Harriet, Nico entertains fanciful ambitions: “I want to be a spy when I grow up, or maybe a fortune teller,” she informs her soon-to-be-employer. “Either way, I’m in training. A pro has to hone her skills.” Nico, too, has a spy outfit — in her case, comprised of a wig and falsies — and an assortment of “spy tools” that include her cell phone and a stamp that allows her to forge her parents’ signature on notes excusing her from school. Like Harriet, Nico hungers for the kind of adventure that’s supposed to be off-limits to girls, skipping school to pursue leads, analyzing a kidnapper’s ransom call, luring bad guys into traps. Most importantly, both girls are students of adult behavior. Both Harriet the Spy and Sexy Voice and Robo include a scene in which the heroine constructs detailed character profiles from a few snippets of conversation. The similarities between these moments are striking. In Fitzhugh’s book, Harriet visits a neighborhood diner, nursing an egg cream while listening to other customers’ conversations: A few weeks ago, Salon columnist Laura Miller offered
A few weeks ago, Salon columnist Laura Miller offered