Poignant — now there’s a word I never imagined I’d be using to describe one of Junko Mizuno’s works, given her fondness for disturbing images and acid-trip plotlines. But Little Fluffy Gigolo Pelu is poignant, a perversely sweet and sad meditation on one small, sheep-like alien’s efforts to find his place in the universe.
The story is simple: on the “cute and pink” planet of Princess Kotobuki, Pelu lives with a beautiful race of women and a “calm but carnivorous giant space hippo.” Pelu has always been aware of how different he is from his fellow Kotobukians, but when he learns that he will never be able to have a family of his own, he falls into a terrible funk, begging the hippo to eat him. When the hippo demurs — Pelu is just too woolly to be appetizing — Pelu borrows the hippo’s magic mirror and teleports to Earth in search of others like him. What Pelu discovers, however, is that Earth women view him as an exotic pet, a companion who’s entertaining but disposable. He careens from one unhappy situation to another, meeting young women who are down on their luck: an aspiring singer with a lousy voice, a homely orphan who’s raising an ungrateful brother, a pearl diver plying her trade in the sewer.
Like Mizuno’s other works, Little Fluffy Gigolo Pelu aims for maximum shock value by depicting cute characters engaged in degenerate behavior: popping pills, doing the nasty in nasty places. Yet Fluffy Gigolo leaves a very different aftertaste than Mizuno’s other manga. Pure Trance, for example, is far less coherent, a set of vivid, Hieronymus Bosch-meets-Hello Kitty set pieces, with doll-like girls binging and purging, brandishing chainsaws, and enduring medical procedures that might give Dr. No pause. One could argue that Pure Trance was intended to point out the absurd lengths to which women go to achieve physical perfection, though one could also argue, as Shaenon Garrity does, that Pure Trance is really a vehicle for Mizuno to draw whatever crazy-ass things popped into her head (i.e. naked, chainsaw-wielding Bratz dolls). Either way, Pure Trance feels like a stunt, its Grand Guignol excesses trumping whatever social commentary might inform the story.
By contrast, Fluffy Gigolo‘s shock tactics serve dramatic and thematic functions, inviting the reader to feel sympathy for Pelu while prompting reflection on pregnancy and motherhood — or perhaps more accurately, the way in which childlessness is dramatized in manga, movies, and soap operas, as if being childless were worse than being afflicted with a terminal disease. “I’m better off dead!” Pelu declares. “I can’t have a baby, and I’ll always be alone for life.” Whether or not Mizuno is striving for deeper social commentary is hard to gauge — after all, her story features copious nudity, drug use, and a teleporting, man-eating space hippo from the Planet of the Dolls — but in Pelu’s odyssey, many readers will recognize the way in which biology, social conditioning, and hormones can prompt us to make compromises in pursuit of motherhood.
LITTLE FLUFFY GIGOLO PELU, VOL. 1 • BY JUNKO MIZUNO • LAST GASP • 168 pp. • RATING: MATURE (NUDITY, SEXUALITY, STRONG LANGUAGE, VIOLENCE, DRUG USE — IN SHORT, THE WORKS)
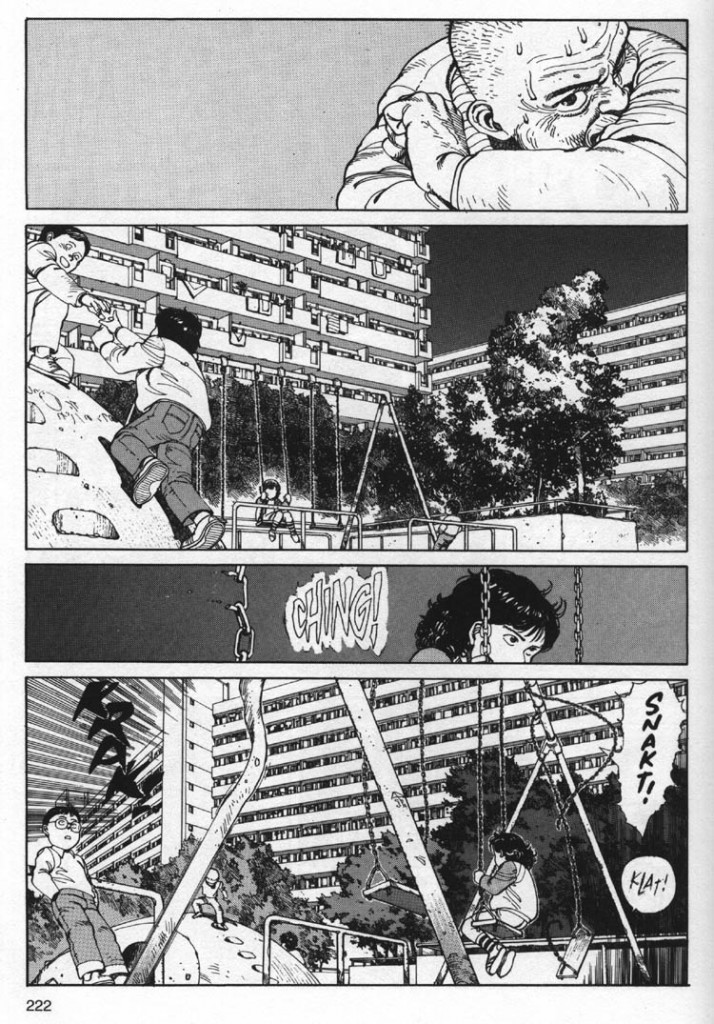
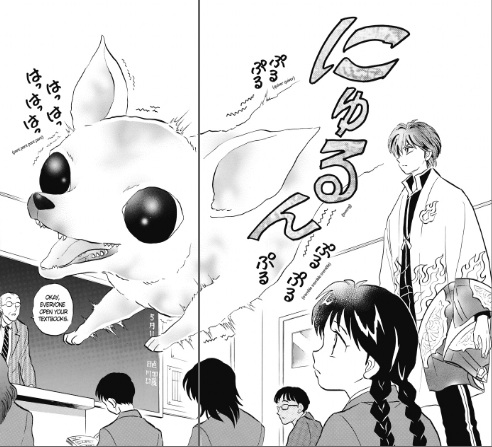
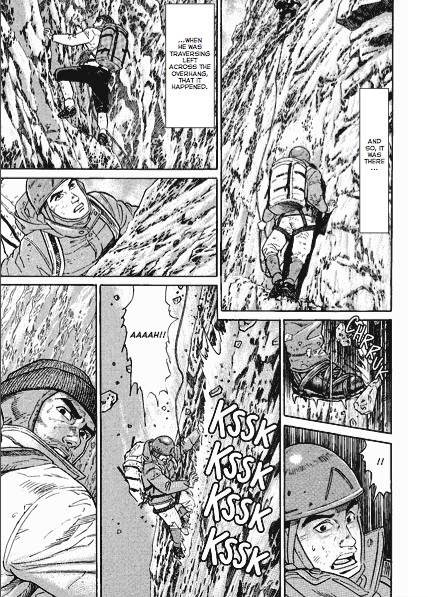




 The humor is good-natured, though Masayuki Ishikawa indulges his inner ten-year-old’s penchant for gross-out jokes every chance he gets.He repeatedly subjects Tadayasu and Kei to Itsuki’s food fetishes, forcing them to watch Itsuki exhume and eat kiviak (a fermented seal whose belly has been stuffed with birds), or try a piece of hongohoe, a form of stingray sashimi so pungent it makes their eyes water. Ishikawa’s decision to render the bacteria as cute, roly-poly creatures with cheerful faces prevents the story from shading into horror, though it’s awfully hard to shake the image of bacteria frolicking in a bed of natto or around the slovenly Misato’s nostril.
The humor is good-natured, though Masayuki Ishikawa indulges his inner ten-year-old’s penchant for gross-out jokes every chance he gets.He repeatedly subjects Tadayasu and Kei to Itsuki’s food fetishes, forcing them to watch Itsuki exhume and eat kiviak (a fermented seal whose belly has been stuffed with birds), or try a piece of hongohoe, a form of stingray sashimi so pungent it makes their eyes water. Ishikawa’s decision to render the bacteria as cute, roly-poly creatures with cheerful faces prevents the story from shading into horror, though it’s awfully hard to shake the image of bacteria frolicking in a bed of natto or around the slovenly Misato’s nostril. 10. Miyuki-chan in Wonderland
10. Miyuki-chan in Wonderland 9. Nightmares for Sale
9. Nightmares for Sale 8. Arm of Kannon
8. Arm of Kannon 7. The Devil Within
7. The Devil Within 6. Dragon Sister!
6. Dragon Sister! 5. The Gorgeous Life of Strawberry-chan
5. The Gorgeous Life of Strawberry-chan 4. J-Pop Idol
4. J-Pop Idol 3. Seraphic Feather
3. Seraphic Feather 2. Innocent W
2. Innocent W 1. Color of Rage
1. Color of Rage


 Though the story is well-executed, the artwork is something of a disappointment. Itsuki goes to great pains to create a diverse cast — a task at which she’s generally successful — but her character designs are generic and dated; I’d be hard-pressed to distinguish the Kimaerans from, say, the cast of RG Veda or Basara. Itsuki also struggles with skin color; her dark-skinned women bear an unfortunate resemblance to kogals, thanks to Itsuki’s clumsy application of screentone.
Though the story is well-executed, the artwork is something of a disappointment. Itsuki goes to great pains to create a diverse cast — a task at which she’s generally successful — but her character designs are generic and dated; I’d be hard-pressed to distinguish the Kimaerans from, say, the cast of RG Veda or Basara. Itsuki also struggles with skin color; her dark-skinned women bear an unfortunate resemblance to kogals, thanks to Itsuki’s clumsy application of screentone.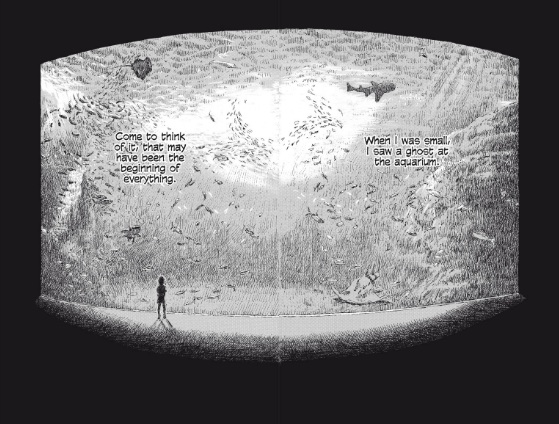
 Though much of the devastation that Hyakkimaru and Dororo witness is man-made (Dororo takes placed during the Sengoku, or Warring States, Period), demons exploit the conflict for their own benefit, holding small communities in their thrall, luring desperate travelers to their doom, and feasting on the never-ending supply of human corpses. Some of these demons have obvious antecedents in Japanese folklore — a nine-tailed kitsune — while others seem to have sprung full-blown from Tezuka’s imagination — a shark who paralyzes his victims with sake breath, a demonic toad, a patch of mold possessed by an evil spirit. (As someone who’s lived in prewar buildings, I can vouch for the existence of demonic mold. Lysol is generally more effective than swordplay in eliminating it, however.) Hyakkimaru has a vested interest in killing these demons, as he spontaneously regenerates a lost body part with each monster he slays. But he also feels a strong sense of kinship with many victims — a feeling not shared by those he helps, who cast him out of their village as soon as the local demon has been vanquished.
Though much of the devastation that Hyakkimaru and Dororo witness is man-made (Dororo takes placed during the Sengoku, or Warring States, Period), demons exploit the conflict for their own benefit, holding small communities in their thrall, luring desperate travelers to their doom, and feasting on the never-ending supply of human corpses. Some of these demons have obvious antecedents in Japanese folklore — a nine-tailed kitsune — while others seem to have sprung full-blown from Tezuka’s imagination — a shark who paralyzes his victims with sake breath, a demonic toad, a patch of mold possessed by an evil spirit. (As someone who’s lived in prewar buildings, I can vouch for the existence of demonic mold. Lysol is generally more effective than swordplay in eliminating it, however.) Hyakkimaru has a vested interest in killing these demons, as he spontaneously regenerates a lost body part with each monster he slays. But he also feels a strong sense of kinship with many victims — a feeling not shared by those he helps, who cast him out of their village as soon as the local demon has been vanquished. For folks who find the cartoonish aspects of Tezuka’s style difficult to reconcile with the serious themes addressed in Buddha, Phoenix, and Ode to Kirihito, Dororo may prove a more satisfying read. The cuteness of Tezuka’s heroes actually works to his advantage; they seem terribly vulnerable when contrasted with the grotesque demons, ruthless samurai, and scheming bandits they encounter. Tezuka’s jokes — which can be intrusive in other stories — also prove essential to Dororo‘s success. He shatters the fourth wall, inserts characters from his stable of “stars,” borrows characters from other manga-kas’ work, and punctuates moments of high drama with low comedy, underscoring the sheer absurdity of his conceits… like sake-breathing shark demons. Put another way, Dororo wears its allegory lightly, focusing primarily on swordfights, monster lairs, and damsels in distress while using its historical setting to make a few modest points about the corrosive influence of greed, power, and fear.
For folks who find the cartoonish aspects of Tezuka’s style difficult to reconcile with the serious themes addressed in Buddha, Phoenix, and Ode to Kirihito, Dororo may prove a more satisfying read. The cuteness of Tezuka’s heroes actually works to his advantage; they seem terribly vulnerable when contrasted with the grotesque demons, ruthless samurai, and scheming bandits they encounter. Tezuka’s jokes — which can be intrusive in other stories — also prove essential to Dororo‘s success. He shatters the fourth wall, inserts characters from his stable of “stars,” borrows characters from other manga-kas’ work, and punctuates moments of high drama with low comedy, underscoring the sheer absurdity of his conceits… like sake-breathing shark demons. Put another way, Dororo wears its allegory lightly, focusing primarily on swordfights, monster lairs, and damsels in distress while using its historical setting to make a few modest points about the corrosive influence of greed, power, and fear.