 First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author.
First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author.
…
 First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author.
First published in 1964, Harriet the Spy featured a radically different kind of heroine than the sweet, obedient girls found in most mid-century juvenile lit; Harriet was bossy, self-centered, and confident, with a flair for self-dramatization and a foul mouth. She favored fake glasses, blue jeans, and a “spy tool” belt over angora sweaters or skirts, and she roamed the streets of Manhattan doing the kind of reckless, bold things that were supposed to be off-limits to girls: peering through skylights, hiding in alleys, concealing herself in dumbwaiters, filling her notebooks with scathing observations about classmates and neighbors. Perhaps the most original aspect of Louise Fitzhugh’s character was Harriet’s complete and utter commitment to the idea of being a writer; unlike Nancy Drew, Harriet wasn’t a goody-goody sleuth who wanted to help others, but a ruthless observer of human folly who viewed spying as necessary preparation for becoming an author. Nico Hayashi, code name “Sexy Voice,” is a bit older than Harriet — Nico is 14, Harriet is 11 — but she’s cut from the same bolt of cloth, as Sexy Voice and Robo amply demonstrates. Like Harriet, Nico entertains fanciful ambitions: “I want to be a spy when I grow up, or maybe a fortune teller,” she informs her soon-to-be-employer. “Either way, I’m in training. A pro has to hone her skills.” Nico, too, has a spy outfit — in her case, comprised of a wig and falsies — and an assortment of “spy tools” that include her cell phone and a stamp that allows her to forge her parents’ signature on notes excusing her from school. Like Harriet, Nico hungers for the kind of adventure that’s supposed to be off-limits to girls, skipping school to pursue leads, analyzing a kidnapper’s ransom call, luring bad guys into traps. Most importantly, both girls are students of adult behavior. Both Harriet the Spy and Sexy Voice and Robo include a scene in which the heroine constructs detailed character profiles from a few snippets of conversation. The similarities between these moments are striking. In Fitzhugh’s book, Harriet visits a neighborhood diner, nursing an egg cream while listening to other customers’ conversations:
Nico Hayashi, code name “Sexy Voice,” is a bit older than Harriet — Nico is 14, Harriet is 11 — but she’s cut from the same bolt of cloth, as Sexy Voice and Robo amply demonstrates. Like Harriet, Nico entertains fanciful ambitions: “I want to be a spy when I grow up, or maybe a fortune teller,” she informs her soon-to-be-employer. “Either way, I’m in training. A pro has to hone her skills.” Nico, too, has a spy outfit — in her case, comprised of a wig and falsies — and an assortment of “spy tools” that include her cell phone and a stamp that allows her to forge her parents’ signature on notes excusing her from school. Like Harriet, Nico hungers for the kind of adventure that’s supposed to be off-limits to girls, skipping school to pursue leads, analyzing a kidnapper’s ransom call, luring bad guys into traps. Most importantly, both girls are students of adult behavior. Both Harriet the Spy and Sexy Voice and Robo include a scene in which the heroine constructs detailed character profiles from a few snippets of conversation. The similarities between these moments are striking. In Fitzhugh’s book, Harriet visits a neighborhood diner, nursing an egg cream while listening to other customers’ conversations:



 The scene: a country road in twelfth-century Japan. The players: Yamato, a bandit with a Robin Hood streak; Dr. Dunstan, a Westerner in sunglasses and a flashy yukata; and Yamato’s gang. The robbers surround Dunstan to search his cart for anything of worth, settling on two large crates. Though Dunstan warns them that the consequences of opening the boxes will be dire — “if you wake them, you will die,” he explains — Yamato ignores his advice, prying off the lids to discover what look like two porcelain boys. Both figures spring to life, with Vice — the “ultimate evil one,” in case you didn’t guess from his name — slaughtering six robbers in short order. Though Yamato is badly outclassed — he has a sword, Vice has a variety of lethal powers that would be the envy of the US military — he vows to defend his friends. Yamato’s brave gesture gives the second doll, Ultimo, an opening to jump into the battle and send Vice packing.
The scene: a country road in twelfth-century Japan. The players: Yamato, a bandit with a Robin Hood streak; Dr. Dunstan, a Westerner in sunglasses and a flashy yukata; and Yamato’s gang. The robbers surround Dunstan to search his cart for anything of worth, settling on two large crates. Though Dunstan warns them that the consequences of opening the boxes will be dire — “if you wake them, you will die,” he explains — Yamato ignores his advice, prying off the lids to discover what look like two porcelain boys. Both figures spring to life, with Vice — the “ultimate evil one,” in case you didn’t guess from his name — slaughtering six robbers in short order. Though Yamato is badly outclassed — he has a sword, Vice has a variety of lethal powers that would be the envy of the US military — he vows to defend his friends. Yamato’s brave gesture gives the second doll, Ultimo, an opening to jump into the battle and send Vice packing.


 Do you remember those first, glorious seasons of Heroes and Lost? Both shows promised to reinvigorate the sci-fi thriller with complex, flawed characters and plots that moved freely between past, present, and future. By the middle of their second seasons, however, it was clear that neither shows’ writers knew how to successfully resolve the conflicts and mysteries introduced in the first, as the writers resorted to cheap tricks — the out-of-left-field personality reversal, the all-too-convenient coincidence, and the arbitrary let’s-kill-off-a-character plot twist — to keep the myriad plot lines afloat, alienating thousands of viewers in the process. Heroes and Lost seemed proof that even the scariest doomsday scenario would fall flat if saddled with too many subplots and secondary characters.
Do you remember those first, glorious seasons of Heroes and Lost? Both shows promised to reinvigorate the sci-fi thriller with complex, flawed characters and plots that moved freely between past, present, and future. By the middle of their second seasons, however, it was clear that neither shows’ writers knew how to successfully resolve the conflicts and mysteries introduced in the first, as the writers resorted to cheap tricks — the out-of-left-field personality reversal, the all-too-convenient coincidence, and the arbitrary let’s-kill-off-a-character plot twist — to keep the myriad plot lines afloat, alienating thousands of viewers in the process. Heroes and Lost seemed proof that even the scariest doomsday scenario would fall flat if saddled with too many subplots and secondary characters. From the very first pages of volume one, Urasawa demonstrates an uncommon ability to move back and forth in time, juxtaposing scenes from Kenji’s past with brief glimpses of the future. The success of these scenes is attributable, in part, to Urasawa’s superb draftsmanship, as he does a fine job of aging his characters from their long-limbed, baby-faced, ten-year-old selves into thirty-somethings weighed down by adult responsibilities.
From the very first pages of volume one, Urasawa demonstrates an uncommon ability to move back and forth in time, juxtaposing scenes from Kenji’s past with brief glimpses of the future. The success of these scenes is attributable, in part, to Urasawa’s superb draftsmanship, as he does a fine job of aging his characters from their long-limbed, baby-faced, ten-year-old selves into thirty-somethings weighed down by adult responsibilities.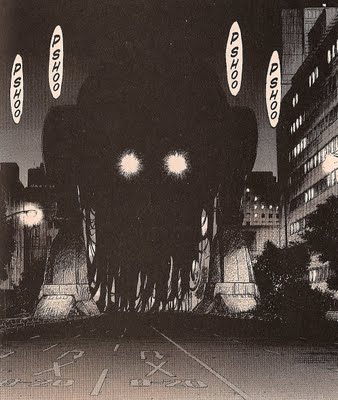



 10. Oishinbo a la Carte
10. Oishinbo a la Carte 




 4. Pluto: Urasawa x Tezuka
4. Pluto: Urasawa x Tezuka

